Journal of Bionic Engineering (2025) 22:1096–1110https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-025-00697-6
Synthesizing IMO-Net with GRU for Sensorless High-precision and Low-latency Jump Landing Detection in Humanoid Robots
Xiaoshuai Ma1 · Han Yu2 · Junyao Gao1 · Xuechao Chen1 · Zhangguo Yu1 · Qiang Huang1
1 School of Mechatronical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Shanghai Flexiv Robotics Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai 200245, China
Abstract
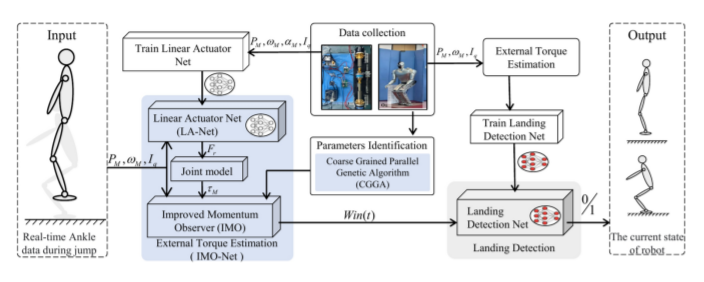
Accurate landing detection is crucial for humanoid robots performing high dynamic motions. Unlike common methods that rely on redundant force-torque sensors and low-precision observers to estimate landing states, this paper proposes a novel landing detection method characterized by high precision and low noise, synthesizing a learning-based Improved Momentum Observer (IMO-Net) for the ankles’ external torque estimation with a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)-based network for state judgment. Since the movement and external torque of the ankle undergo drastic changes during high dynamic motions, achieving accurate and real-time estimation presents a challenge. To address this problem, IMO-Net employs a new Improved Momentum Observer (IMO), which does not depend on acceleration data derived from secondorder differentials or friction model, and significantly reduces noise effects from sensors data and robot foot wobble. Furthermore, an Elman network is utilized to accurately calculate the ankle output torque (IMO input), significantly reducing the estimation error. Finally, leveraging IMO-Net and extensive experimental data, we developed and optimized a GRUbased landing detection network through comprehensive ablation experiments. This refined network reliably determines the robot’s landing states in real-time. The effectiveness of our methods has been validated through experiments.
Keywords External torque estimation · Landing detection · Improved momentum observer · GRU-based
Copyright © 2025 International Society of Bionic Engineering All Rights Reserved
吉ICP备11002416号-1









